Options trading involves various intricate and crucial components like option Greeks that every trader must know. These Greeks, derived from mathematical models, represent the sensitivity of an option's price to changes in various market parameters. Among these, Gamma holds significant importance, particularly for options traders who frequently adjust their positions (especially with Delta).
What is Gamma?
Gamma measures the rate of change of an option's Delta with respect to a change in the underlying asset's price. In simpler terms, it quantifies how quickly an option's Delta (sensitivity to price changes) changes as the underlying asset's price fluctuates.
Why is Gamma Important?
Gamma plays a pivotal role in options trading for several reasons:
- Accelerating Profits and Losses: Gamma has both accelerating power on profits and losses within the trade of options. A high Gamma would mean that the option's Delta changes faster with small changes in price. This high sensitivity may lead to high gains, assuming that the market moves in your favour since the option value would increase at a faster rate. At the same time, it can also lead to huge losses if the market works against you, as the price value of the option would rapidly decline.
- Managing Risk: Traders must be aware of Gamma while trading options. By understanding the impact of Gamma on Delta, traders may be able to predict the way positions will react to a price change. This provides an opportunity to adjust strategies, like rebalancing portfolios or using hedging techniques, to keep the level of exposure to risk within limits in order to avoid unpredictable losses due to a sudden shift in the market.
- Options Strategies: Gamma is a key factor in most strategies involving options, including volatility trading, delta-neutral strategies, and calendar spreads. Under volatility trading, Gamma reflects the price of an option and how it will be impacted by the changes in market volatility. High Gamma implies frequent adjustments of delta-neutral strategies to keep them neutral with respect to directional risk. For calendar spreads, Gamma affects how the spread value changes over time. In terms of monetary reality, this impacts how the strategy works.
Calculating Gamma
Gamma for a given option is calculated as:
Gamma = Change in Delta / Change in Underlying Price
Seasoned options traders usually use complex options pricing models like the Black Scholes Option Pricing Model to calculate the gamma. Using these models can be a little complex for beginners as it involves various factors like standard deviation, risk-free rate of return, dividend yield, strike price, etc.
Luckily, options traders can now use customised tools like Tradejini’s Scalper Mode to calculate gamma within seconds. These tools consider factors such as implied volatility (IV), time decay, strike price, and dividend yields to provide real-time Gamma calculations. This simplifies the process and allows traders to quickly assess the Gamma exposure of their positions.
Basic Example of Delta and Gamma
Let’s consider this example to understand the workings of Delta and Gamma:
- Nifty spot = 23,300
- Strike = 23,400
- Option type = CE
- Premium = Rs.16/-
- Delta = 0.2
- Gamma = 0.0025
- Change in spot = 50 points
- New spot price = 23,300 + 50 = 23,350
So, what will the new premium and Delta be with this change in spot price? Let’s find out -
- Change in premium = Delta x Change in spot = 0.2 x 50 = 10
- New premium = 10 + 16 = 26
- Change in Delta = Gamma x Change in underlying = 0.0025 x 50 = 0.125
- New Delta = Old Delta + Change in Delta = 0.2 + 0.125 = 0.325
When Nifty moved from 23,300 to 23,350, the 23,400 CE premium changed from Rs.16 to Rs.26, and along with this, the Delta changed from 0.2 to 0.325.
Now, assume Nifty moves up another 50 points from 23,350; let’s see what happens with the 23,400 CE option -
- Old spot = 23,350
- New spot value = 23,350 + 50 = 23,400
- Old Premium = 26
- Old Delta = 0.325
- Change in Premium = 0.325 x 50 = 16.25
- New Premium = 26 + 16.25 = 42.25
- Change in delta =0.0025 x 50 = 0.125
- New Delta = 0.325 + 0.125 = 0.45
Now, you must be wondering why the Gamma value is constant in the above example. In reality, the Gamma value also changes with the change in the price of the underlying asset.
How Gamma Changes with IV, Time and Strike Price
IV, Time Decay and Gamma
Gamma tends to increase as an option approaches expiration, especially for at-the-money (ATM) options. However, this may not always be the case. The impact of time decay on Gamma is influenced by other factors like implied volatility (IV). Here’s how-
- High IV: When IV is high, Gamma tends to increase as expiration approaches. This is because a high IV implies increased uncertainty about future price movements, making the option's price more sensitive to changes in the underlying asset's price.
- Low IV: When IV is low, Gamma may decrease as expiration approaches. This is because low IV implies less uncertainty about future price movements, making the option's price less sensitive to changes in the underlying asset's price.
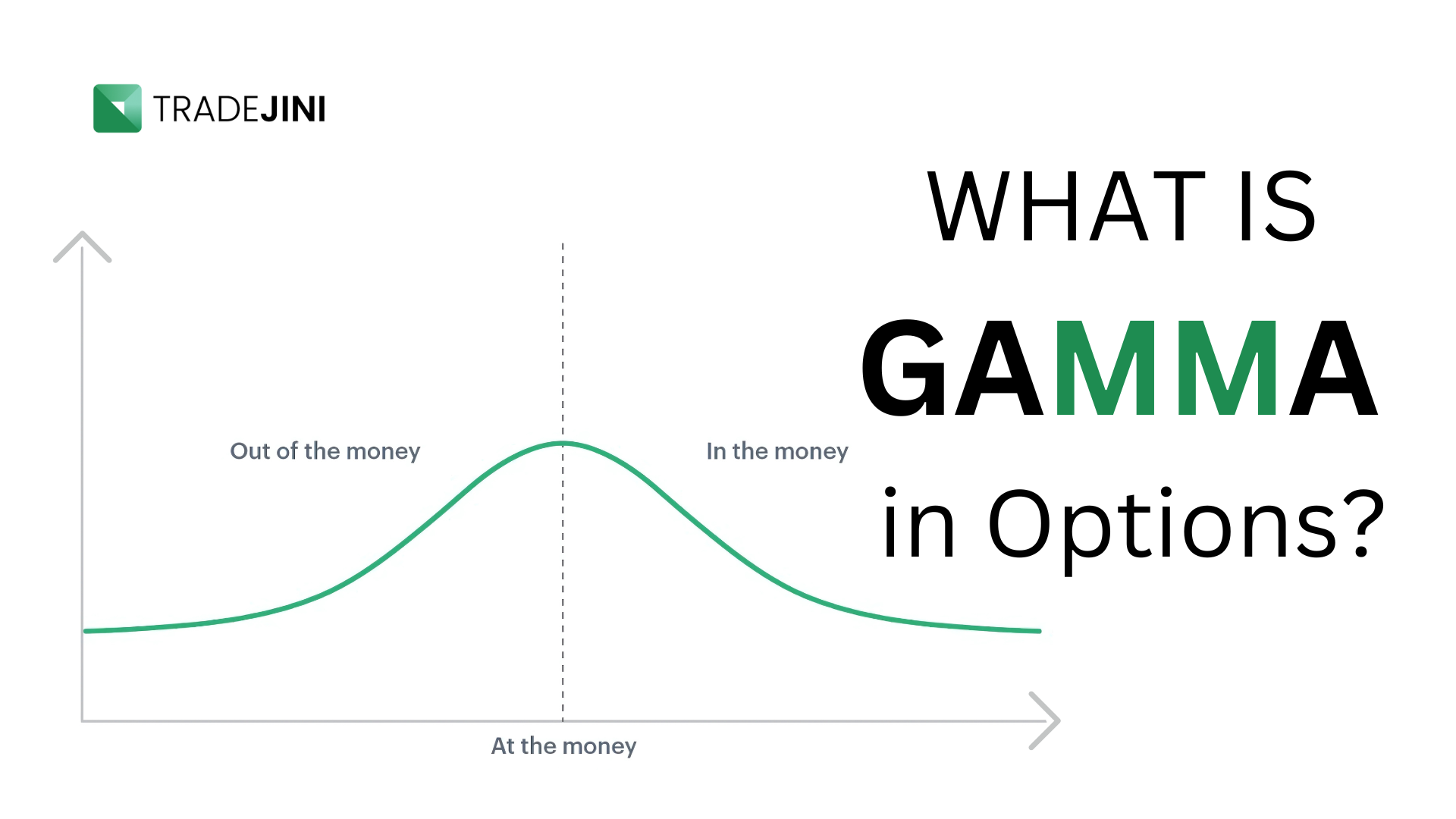
Strike Price and Gamma
- At-the-Money (ATM) Options: Options with strike prices close to the current market price of the underlying asset (ATM options) tend to have the highest Gamma. This is because small changes in the underlying asset's price can have a significant impact on the option's price.
- Out-of-the-Money (OTM) Options: OTM options have lower Gamma compared to ATM options. This is because OTM options are less sensitive to changes in the underlying asset's price.
- In-the-Money (ITM) Options: ITM options also have lower Gamma compared to ATM options. However, as an ITM option approaches expiration, its Gamma can increase due to time decay and the increasing probability of the option being exercised.
Strategies to Manage Gamma
To effectively manage Gamma exposure, you can consider the following strategies:
- Hedging: By adjusting the Delta of your portfolios, you can manage the impact of Gamma on your positions, typically by adding or removing units of the underlying asset to offset potential movements.
- Calendar Spreads: By combining options with different expiration dates, you can create positions with specific Gamma profiles. This can be useful for managing Gamma over time, especially as options approach expiration.
- Gamma Scalping: You can employ gamma scalping to capitalise on small price movements by constantly rebalancing your positions. This can help minimise the impact of rapid price changes on Delta and manage Gamma risk.
Gamma Scalping
Gamma scalping is a trading strategy that involves taking advantage of the rapid price movements of high-Gamma options. Traders who employ this strategy aim to profit from small price fluctuations in the underlying asset.
When to Use Gamma Scalping
Gamma scalping is best used in high-volatility environments where frequent price movements provide opportunities to profit from rebalancing Delta. This strategy can be particularly useful around major events like quarterly earnings reports, RBI announcements, or general elections, when price swings are common.
Risks Associated with Gamma in Options Trading
While Gamma can be a powerful tool for both profit and risk management, it also presents significant risks. Here are some of the key risks associated with Gamma:
- Accelerated Price Movements: High Gamma positions can amplify both profits and losses.
- Time Decay and Gamma: Time decay can accelerate losses in high-Gamma positions.
- Volatility and Gamma: Increased volatility can increase Gamma, but it will also lead to significant losses.
- Over-adjusting: Excessive adjustments to manage Gamma can result in transaction costs that eat into profits, especially in markets with high brokerage fees.
Managing Gamma Risk
- Hedging Strategies: Employing hedging strategies, such as calendar spreads and vertical spreads, can help mitigate Gamma risk.
- Monitor Market Volatility: Keep a close eye on stock market volatility and adjust your positions accordingly.
- Use Stop-Loss Orders: Place stop-loss orders to limit potential losses.
- Use Options Analysis Tools: Utilise software and platforms like Tradejini’s CubePlus app to get detailed Gamma calculations and visualisations.
- Stay Informed: Keep up with market news and economic events that may affect the underlying asset's price.
- Start Small and Learn Gradually: Start with straightforward options strategies to build insight and understanding. As your confidence grows, consider increasing the lot size of the strategy.
- Continuous Learning: The options market is constantly evolving. Stay updated with the latest trends and techniques.
Conclusion
Gamma is a powerful tool for options traders to understand and manage risk. By carefully considering the impact of Gamma on your positions, you can make informed decisions and optimise your strategies. However, it is important to remember that Gamma is just one piece of the puzzle. Mastering Gamma requires patience, continuous learning of technical concepts like price action, demand and supply, volume, etc., and a lot of practical experience.
With the right knowledge and tools, you can manage your Gamma exposure and use it to optimise your portfolio performance, paving the way for a more disciplined and profitable trading approach. So, if you are looking to learn more about options trading, consider Tradejini! With Tradejini's CubePlus app, you can have access to the Scalper Mode, which can be of great help to scalp Gamma and master options trading with its one-click entry-exit feature.
It’s time to take full control of your trades. Download the CubePlus app today!